|
Sypnoides Hampson
Type
species: mandarina Leech, China, India.
Synonyms: Hyposypnoides
Berio,
(type species: flandriana Berio, Za�re); Pysnoides Berio (type
species: mandarina); Supersypnoides Berio (type
species erebina Hampson, China).
Sypnoides
was
divided into three subgenera by Berio & Fletcher (1958), but all share the
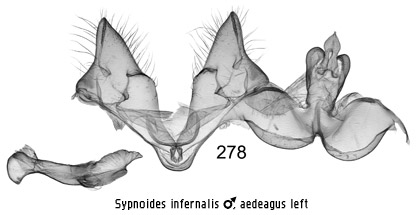
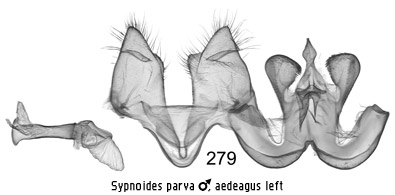
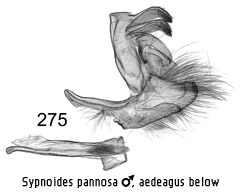
presence of a pair of massive structures from the tegumen that flank the uncus
that could be termed socii. These are best displayed when the genitalia are
mounted opened out after separating the vinculum from the tegumen on one side
(Figs 278, 279). They can also be mounted laterally (Fig 275). The male
antennae are fasciculate.
In the
male abdomen, the eighth segment is narrowed to a ring that bears a fringe of
hairs. The valves are variable in shape, but the flange is central when it
occurs. The saccus is relatively short except in the typical subgenus. The
aedeagus often has the ductus ejaculatorius inserted basally.
The
female genitalia are typical of the Sypna group.
Berio
& Fletcher recognised three subgenera. The typical one and Hyposypnoides Berio
(exclusively African) have spined tibiae, whereas those of subgenera Supersypnoides Berio, the bulk
of the genus, have them unspined. The first species described below belongs to
the typical subgenus, the rest to Supersypnoides. Most of the
latter have a characteristic filigree delineation of the medial area of the forewing
with pale, narrow fasciae as illustrated for the Bornean species.
Sugi
(1987) illustrated the larvae of three Japanese species. They are long,
slender, with the anal prolegs splayed and those on A3 and, to a lesser extent,
A4 reduced. The section between the thorax and A4 is greatly extended, and the
head is large relative to the width of the thoracic segments. The patterns tend
to be longitudinal bands and markings for crypsis. The pupa lacks any bloom in
two Indian species discussed by Sevastopulo (1946, 1947). It occurs in a
spun-together leaf.
Host
plants noted for the genus (Sevastopulo, 1946, 1947; Sugi, 1972, 1987; Robinson et
al.,
2001) are Fagus, Quercus (Fagaceae) and Malus, Rosa and Rubus (Rosaceae).
<<Back
>>Forward <<Return to Content Page
|